In the crypto narrative of 2026, the combination of AI and physical infrastructure (DePIN)—known as "Embodied AI"—is becoming the new battleground. The market is no longer satisfied with mere hype concepts but is starting to look for practical application scenarios.
This article selects three of the most popular and representative projects in the current landscape: peaq, PrismaX, and OpenMind. They occupy three different niches in the robot economy. We will move beyond marketing rhetoric and analyze their current status and potential through actual data and case studies.
TL;DR
- peaq ($PEAQ): Focuses on network infrastructure and asset tokenization. Its core appeal is "Real Yield," with automated farms in its ecosystem already distributing cash flow to NFT holders. Current market cap is approximately $35 million, viewed by the market as an undervalued infrastructure asset.
- PrismaX: Focuses on AI training data and human-robot collaboration. Its core appeal is the backing of a $11 million funding round led by a16z, and the airdrop expectation of "earning points by remotely controlling robots." It addresses the scarcity of "physical world interaction data" for robots.
- OpenMind ($ROBO): Focuses on the operating system and application distribution. Its core appeal is the narrative of being the "Android system for robots" and the controversy over its high valuation with a $400 million FDV. It aims to establish a unified standard for robot app stores.
1. @peaq : The Layer-1 Network That Enables Machines to Earn
Positioning: A Layer-1 blockchain designed for the Machine Economy. Core Logic: Machines are not just tools but economic entities capable of owning wallets, signing transactions, and earning income. This is akin to turning every device into an automated earning agent.
Concrete Case 1: Tokenized "Robot Farm"
While most DePIN projects are still selling nodes, peaq has presented a case that generates actual cash flow.
In late 2025, a project on the peaq ecosystem launched the world's first tokenized robot farm in Hong Kong, using automated robots for hydroponic vegetable cultivation. Its operation logic is straightforward:
- Users purchase NFTs representing shares of the farm.
- Farm robots work, growing and selling vegetables.
- Revenue generated from sales (real-world fiat income) is converted into stablecoins.
- Earnings are distributed directly on-chain to NFT holders.
According to on-chain data and community feedback, the farm completed its first earnings distribution at the end of January 2026:
- Distribution Amount: A single large holder reported earnings of approximately 3820 USDT.
- Annualized Yield (APY): Early participants estimated it to be around 18%.
This model of "earning not through token inflation, but by selling vegetables" is a significant boost of confidence for current crypto investors seeking stability and low risk, serving as a tangible case of RWA (Real World Assets) implementation.
Concrete Case 2: Partnerships & Industrial-Grade Validation
peaq has partnered with several commercial giants:
- Bosch: Collaboration focuses on IoT sensors and decentralized identity (peaq ID), testing automatic data recording by devices on-chain. Future possibilities include appliances or industrial equipment leaving the factory with built-in "wallets".
- Mastercard: Exploring payment gateway integration to connect traditional fiat systems with peaq's machine wallets (e.g., paying with a credit card after an electric vehicle charges, with settlement via peaq in the background).
- Airbus: Previously tested supply chain tracking.
These collaborations are currently more about technical proof-of-concept (PoC) and have not yet generated massive commercial revenue at scale. However, they demonstrate that peaq's technical standards meet industrial-grade security requirements, a claim few other projects can match.
Fundamentals & Market Performance (Data as of 2026-02-15)
- Current Price: ~$0.019
- Circulating Market Cap (MC): ~$34.25 million
- Fully Diluted Valuation (FDV): ~$78 million
- Ecosystem Scale: 50-60+ DePIN applications are currently running or in development. The ecosystem connects over 2 million to 5.2 million physical devices, robots, and sensors. Industry coverage spans 21-22 sectors, including mobility (EV charging, navigation), energy, telecommunications, agriculture, and smart cities.
- Risk Points: As a Layer-1, the token is primarily used for Gas and staking, requiring ecosystem application growth to support the price; the total supply is large (~4.3 billion), potentially facing inflationary pressure.
peaq's advantage lies in its proven commercial closed-loop and backing by industrial giants. With an FDV under $100 million, its valuation is relatively low compared to other AI infrastructure projects, making it suitable for stable allocations for those bullish on infrastructure.
2. @PrismaXai : The Data Goldmine Backed by a16z
Positioning: An AI robot data layer based on human-robot collaboration (RLHF). Core Logic: Making robots smarter requires vast amounts of data. PrismaX allows ordinary people to remotely control robots to complete tasks, thereby generating high-quality training data, and provides incentives to users. This solves the "last mile" problem for AI models—the leap from digital intelligence to physical intelligence.
Concrete Case: Remote Operation (Teleoperation)
PrismaX builds a platform for users to remotely control real robotic arms (e.g., devices in a lab) via a web page:
- Users operate the robotic arm to perform actions (e.g., moving objects).
- The system records the operation data.
- Data is sold to robotics companies to train AI.
- Users earn points, redeemable for future tokens.
This "Play-to-Train" model differs from traditional "compute mining" as it requires real user effort, resulting in higher data value and creating a data flywheel: More participants → More data → Better models → More efficient operations → More participants.
Fundamentals & Market Performance (Data as of 2026-02-15)
- Funding Background: Raised $11 million in a seed round led by top-tier VC a16z, with participation from Virtuals Protocol.
- Current Stage: Points system and airdrop anticipation phase. Users can earn points through daily check-ins, whitepaper quizzes, and paid training ($99).
- Ecosystem Scale: Over 500 participants have completed remote robotic arm operations, covering multiple global locations. Operable Robotic Arms: 2 full systems launched (Unitech Walker "Tommy" and "Bill"), available for direct user interaction.
- Risk Points: Currently, many "airdrop farming studios" are rushing in to farm points. If the project team cannot effectively filter high-quality training data, these points will become worthless, ultimately leading to severe selling pressure during the airdrop redemption. There is still industry debate on whether the data quality from remote operations can truly train commercial-grade robots.
PrismaX's core attraction lies in leveraging a16z's backing + a unique "data flywheel" mechanism to切入 the most scarce part of robot training with a zero-cost participation model. The a16z backing and unique mechanism make it an early Alpha opportunity.
3. @openmind_agi : The Android System for Robots
Positioning: A universal operating system (OS) and app store for robots. Core Logic: Solves the problem of robot hardware fragmentation, allowing developers to write code once and run it on robots from different brands (e.g., Unitree, Fourier), similar to the Android system in the mobile phone industry.
Concrete Case: App Store Taking Shape
OpenMind has already launched an app store and recently announced partnerships with 10 embodied AI companies, primarily leading manufacturers in China and the US, such as:
- Unitree: A leader in the field of robotic dogs.
- Fourier Intelligence: Focuses on humanoid robots.
- UBTECH: The first listed company for humanoid robots.
- Deep Robotics: Industrial-grade quadruped robots.
Details: https://x.com/openmind_agi/status/2015671520899817620?s=20
According to multiple official reports from late January and early February 2026, the OpenMind Robot App Store launched with 5 real-time running applications, focusing on core areas such as: Autonomous Mobility, Social Interaction, Privacy Protection, Education and Skill Training, etc.
Although the number of available hardware units is currently small, it proves that its technical logic of "cross-hardware operation" is viable.
Fundamentals & Market Performance (Data as of 2026-02-15)
- Latest Funding Round: Participated in by top-tier institutions like Pantera Capital, Sequoia China.
- Previous Round Valuation: Approximately $200 million
- Kaito Launchpad Presale Valuation: $400 million FDV (double the premium)
- Ecosystem Scale: App Store Applications: 5+ (as of end of January); Hardware Partners: 10+ international/domestic leading manufacturers; Over 1,000 developers have joined the ecosystem globally.
- Risk Analysis: High Valuation, Low Float: The high opening valuation of $400 million FDV is considered high, potentially透支 secondary market upside, and faces pressure from early VC unlocks. Competition from Giants: Traditional robot manufacturers (e.g., Tesla Optimus) tend to prefer closed systems (like Apple's iOS). Whether OpenMind's open-source Android model can survive among giants depends on its ability to attract enough mid-to-small tier manufacturers.
OpenMind is currently in a strategic phase of "small entry point, broad compatibility, high ceiling." Although the number of applications is still in its infancy, it has achieved coverage of 10 hardware manufacturers downstream and built a technical foundation upstream with a thousand developers. Its true potential lies in providing a unified cognitive layer for global hardware and leveraging a decentralized network to solve the most challenging data problems in AI training. A future where skills can be updated like on a phone and knowledge shared between machines is already beginning to take shape through this App Store.
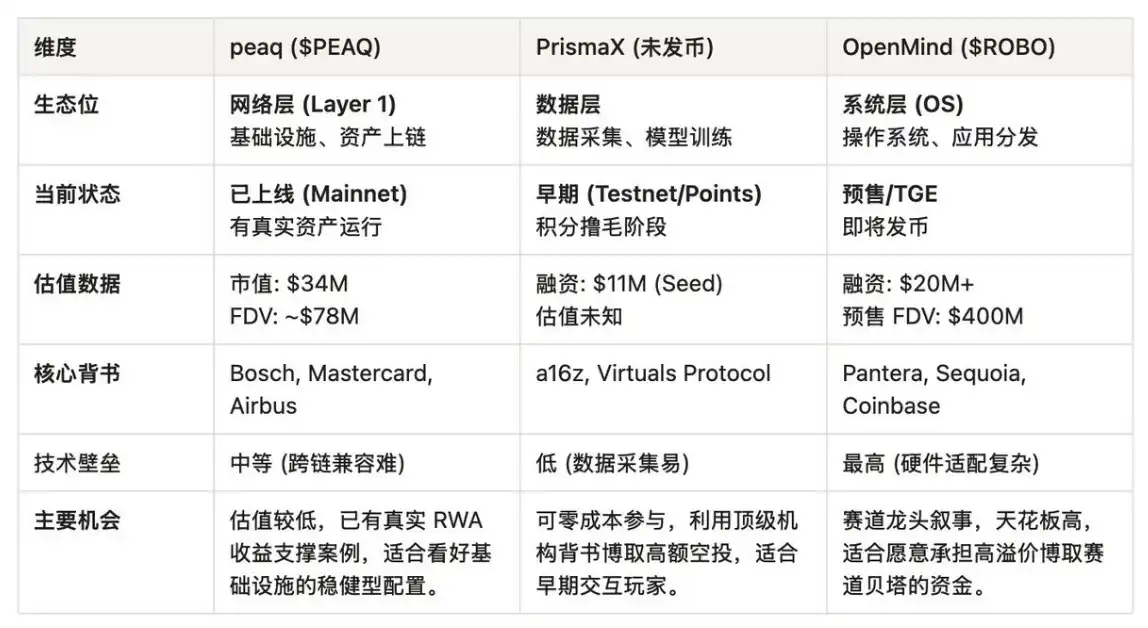
Comprehensive Comparative Analysis
To more intuitively understand the differences between these three projects, we provide a横向 comparison across core dimensions:
In 2026, decentralized "embodied AI" applications are no longer a concept but a reality in the making. The three projects analyzed in this article恰好 represent the most representative three niches in this emerging track—the network layer, the data layer, and the system layer.
Imagine a scenario at the end of 2026: a robot is working on an automated farm. The efficient operation of this robot requires support from three levels:
1 Data Support (PrismaX): How did it learn "how to farm"? Through remote operators on PrismaX teaching it. Teleoperation data from 1000 global operators allows the AI model to learn complete agricultural operation logic.
2 System Support (OpenMind): What brand is this robot? How does it compete with other brands? It runs on OpenMind OS and can download "Agricultural Optimization Apps" from the App Store, competing with robots from different brands on the same system.
3 Network Support (peaq): How is the money earned by this robot distributed? The USDT generated from the farm's sales of hydroponic vegetables is automatically settled through peaq's network smart contracts and distributed to owners according to their NFT shares.
These three layers are indispensable. Without PrismaX's data, robots cannot become smarter; without OpenMind's system, applications cannot be deployed cross-platform; without peaq's incentives, participants lack the drive to sustain the entire cycle.
Conversely, when these three layers collaborate, they create a positive feedback loop—increased participation → improved data quality → better application performance → higher economic incentives → attracting more participants. This is the core value of Web3's integration with the physical world.
The opportunity in the 2026 robot track lies not in which project will be the "winner," but in how these three layers collaborate to move embodied intelligence from concept to scalable application.